Database
Currently, Nestipy includes a module designed to facilitate database interactions. This module offers tools and functionalities to manage database connections, perform queries, and handle data efficiently, making it easier for developers to integrate database operations within their applications.
NestipyDB
NestipyDB is the official database module for Nestipy. It is built on top of Edgy and designed to be modular and configurable.
Installation
NestipyDB depends on Edgy. Make sure to follow the Edgy installation guide to set up dependencies for your specific database.
Usage
First, in your app_module.py, replace the url in DbConfig with your own:
from nestipy.common import Module
from nestipy_db import DbConfig, DbModule,AdminConfig
@Module(
imports=[
DbModule.for_root(
DbConfig(
url="sqlite:///db.sqlite",
models=[],
admin=AdminConfig(enable=True, url="/admin"), # if you need admin dashboard for model
)
),
# other modules...
]
)
class AppModule:
...
To load the config asynchronously, use DbModule.for_root_async:
from typing import Annotated
from nestipy.common import Module
from nestipy.ioc import Inject
from nestipy_config import ConfigModule, ConfigService, ConfigOption
from nestipy_db import DbConfig, DbModule
async def get_db_config(config: Annotated[ConfigService, Inject()]):
return DbConfig(
url=config.get("DATABASE_URL"),
models=[]
)
@Module(
imports=[
ConfigModule.for_root(ConfigOption(), is_global=True),
DbModule.for_root_async(
factory=get_db_config,
inject=[ConfigService]
),
# other modules...
]
)
class AppModule:
...
Models
Every model must be decorated with Model and must extends BaseModel from nestipy_db
from datetime import datetime
from uuid import UUID, uuid4
import edgy
from ..user.user_model import User
from nestipy_db import BaseModel, Model
@Model()
class Post(BaseModel):
id: UUID = edgy.UUIDField(primary_key=True, default=uuid4, editable=False)
title: str = edgy.CharField(max_length=256, default="")
user: User = edgy.ForeignKey(User, on_delete=edgy.CASCADE, related_name="posts")
reaction: list[User] = edgy.ManyToManyField(
User, through_tablename=edgy.NEW_M2M_NAMING
)
created_at: datetime = edgy.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
updated_at: datetime = edgy.DateTimeField(auto_now=True)
Note
Note that, you need to register all of your models inside DbConfig(..., models=[]) or by importing DbModule.for_feature(Model1, Model2) in your current module.
CLI
NestipyDB aliases Edgy CLI commands and adds support for model generation.
Instead of using edgy, use:
NestipyDB introduces a new model generation command:
module_nameis optional.- If omitted,
model_namewill also be used as themodule_name. - The model will be created inside the specified module, or the module folder will be created if it doesn't exist.
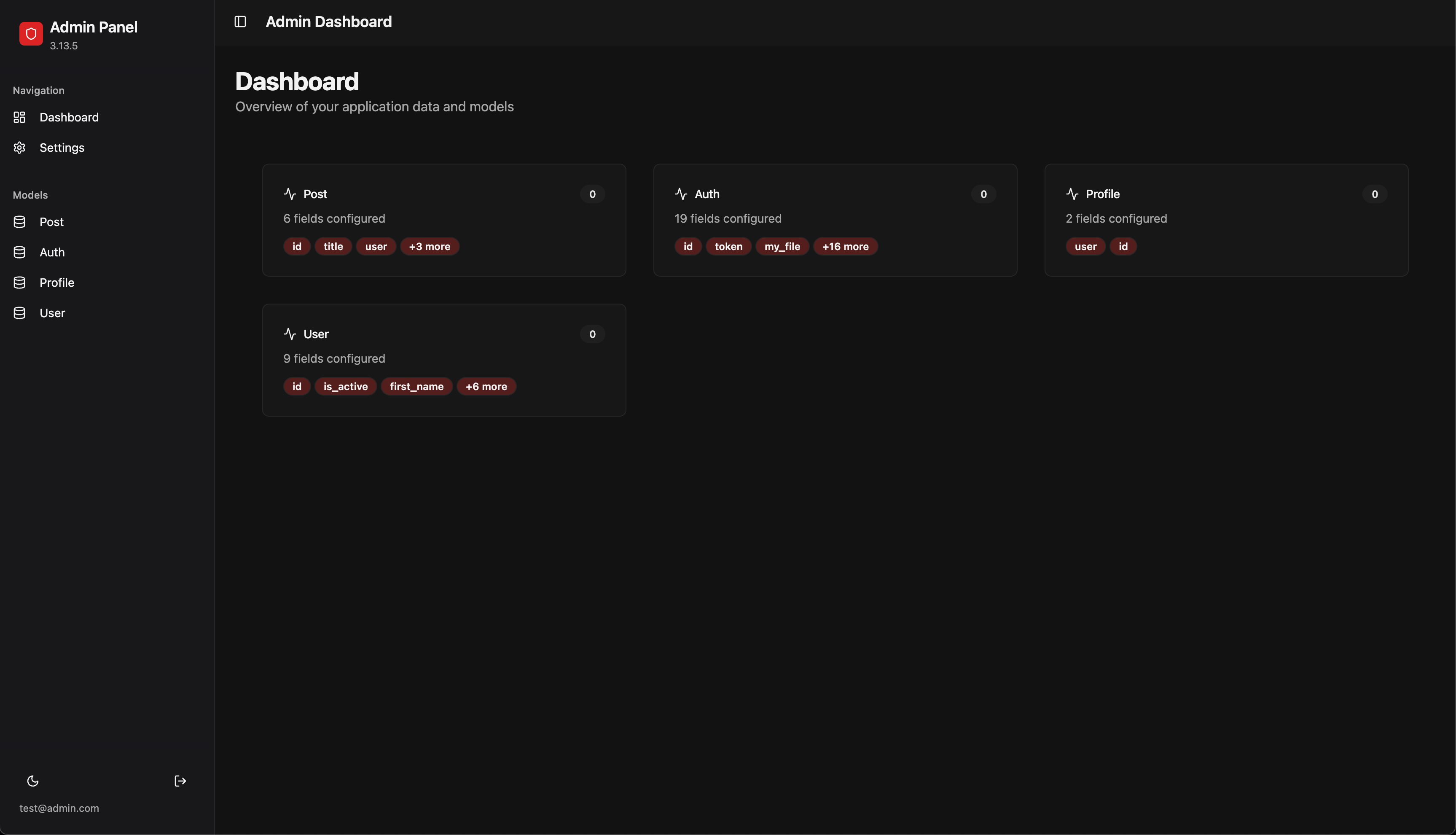
Admin
If admin is enabled, you can access it with the url specified in AdminConfig.
The default credential for login is email: test@admin.com,password: admin.
You can override this via AdminConfig.
Other options are also available.
Support us
Nestipy is a project released under the MIT license, meaning it's open source and freely available for use and modification. Its development thrives with the generous contributions of these fantastic individuals.